动态资产定价代写 Dynamic Asset Pricing代写 三项式定价代写
626Dynamic Asset Pricing Homework 1 Bruno Dupire 动态资产定价代写 1) Trinomial pricing In this economy, a stock and a bond can be freely traded (bought or sold short). Initial dollar price of t...
View detailsSearch the whole station
国际商业金融课业代写 1. Comparative advantage Exercises 1.1 to 1.5 Illustrate an example of trade induced by comparative advantage under the following assumptions:
Exercises 1.1 to 1.5
Illustrate an example of trade induced by comparative advantage under the following assumptions: assume that China and France each have 1,000 production units. With one unit of production (a mix of land, labour, capital, and technology), China can produce either 10 containers of toys or 7 cases of wine. France can produce either 2 containers of toys or 7 cases of wine. Thus, a production unit in China is five times as efficient compared to France when producing toys, but equally efficient when producing wine. Assume at first that no trade takes place. China allocates 800 production units to building toys and 200 production units to producing wine. France allocates 200 production units to building toys and 800 production units to producing wine.
What is the production and consumption of China and France without trade?
Assume complete specialization, where China produces only toys and France produces only wine.
What would be the effect on total production?
China’s domestic price is 10 containers of toys equals 7 cases of wine. Assume China produces 10,000 containers of toys and exports 2,000 to France. Assume France produces 7,000 cases of wine and exports 1,400 cases to China. What happens to total production and consumption?
France’s domestic price is 2 containers of toys equals 7 cases of wine. Assume China produces 10,000 containers of toys and exports 400 containers to France. Assume France in turn produces 7,000 cases of wine and exports 1,400 cases to China. What happens to total production and consumption?
What happens to total production and consumption? First calculate the mid-price for exchange and then show what happens to total production and consumption.
Consider the no trade input and output situation presented in the table below for countries X and Y. Assuming that free trade is allowed, develop a scenario that will benefit the citizens of both countries.
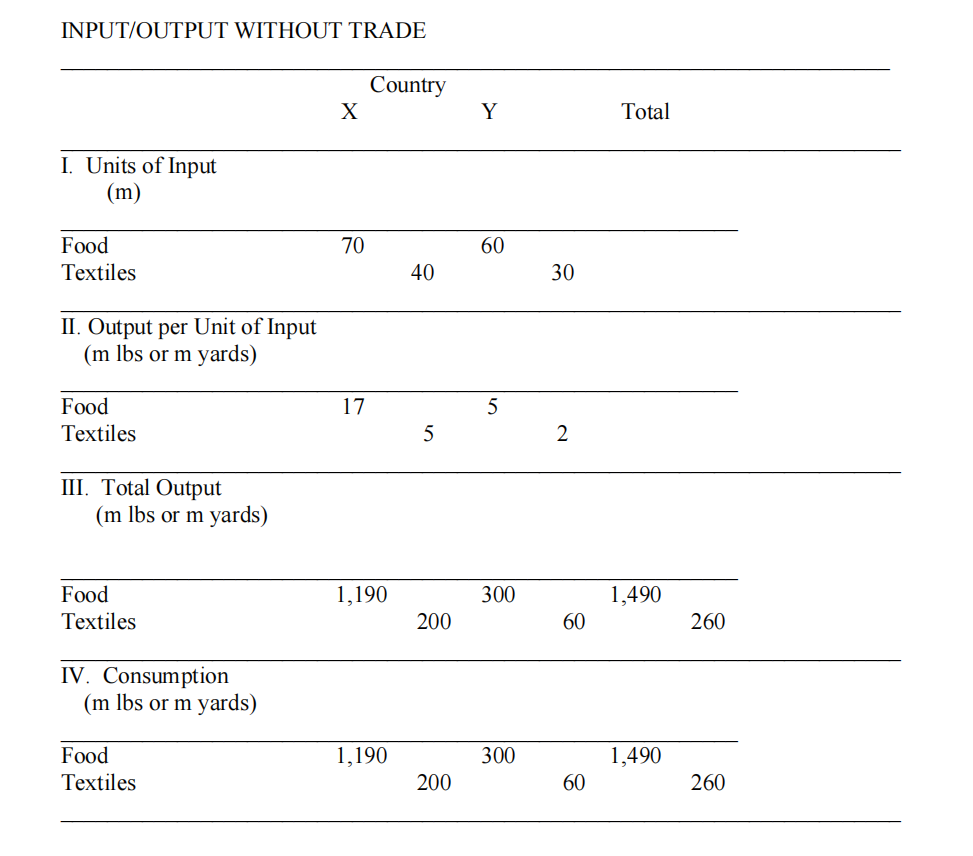
Explain the considerations that might limit the extent to which the theory of comparative advantage is realistic.

更多代写:代做c/c++语言作业 托福线上考试作弊 英国工科作业代写 电子工程essay代写 电影专业report代写 加拿大大学网课
合作平台:essay代写 论文代写 写手招聘 英国留学生代写
Dynamic Asset Pricing Homework 1 Bruno Dupire 动态资产定价代写 1) Trinomial pricing In this economy, a stock and a bond can be freely traded (bought or sold short). Initial dollar price of t...
View details代写代考安全吗?被发现了会被抓起来吗? 代写代考 留学生在国外的学习过程的压力都是非常的大的,很多留学生都害怕自己最后毕不了业,让自己的时间白白的浪费,还浪费了家里的资金,非常的郁闷,为了能够顺...
View detailsFINS3616 – International Business Finance iLab Assignment 国际商业金融代写 Weighting This assessment is worth 15% of your final grade for FINS3616 – International Business Finance. Next ...
View detailsIEOR 4700 Homework 10: Wednesday April 7 2021 金融工程作业代写 Problem 2. [25 points] Assume the continuously compounded spot rates of Problem 1. Find the value of an FRA that enables the h...
View details