统计quiz代考 sta130代写 统计考试代考 统计作业代做
398W6: Weekly quiz 统计quiz代考 Quiz Instructions This quiz will cover the asynchronous content from the Week 6 module. It is due BEFORE our synchronous class. Quiz Instructions This quiz ...
View detailsSearch the whole station
exam统计代考 Note: During the test only the use of a sheet with formulas and a calculator areallowed. QUESTION 1 (5,0) Punctuality in meetings is a worrying
Note: During the test only the use of a sheet with formulas and a calculator areallowed.
(5,0) Punctuality in meetings is a worrying factor for many Portuguese companies. To evaluate the time of delay at the beginning of the meetings, Company AB decided to collect data on this subject in its two subsidiaries, Empresa A located in Lisbon and Empresa B located in Porto. The following results were presented by Empresa A relative to the delays (in minutes) verified in the last 58 meetings.
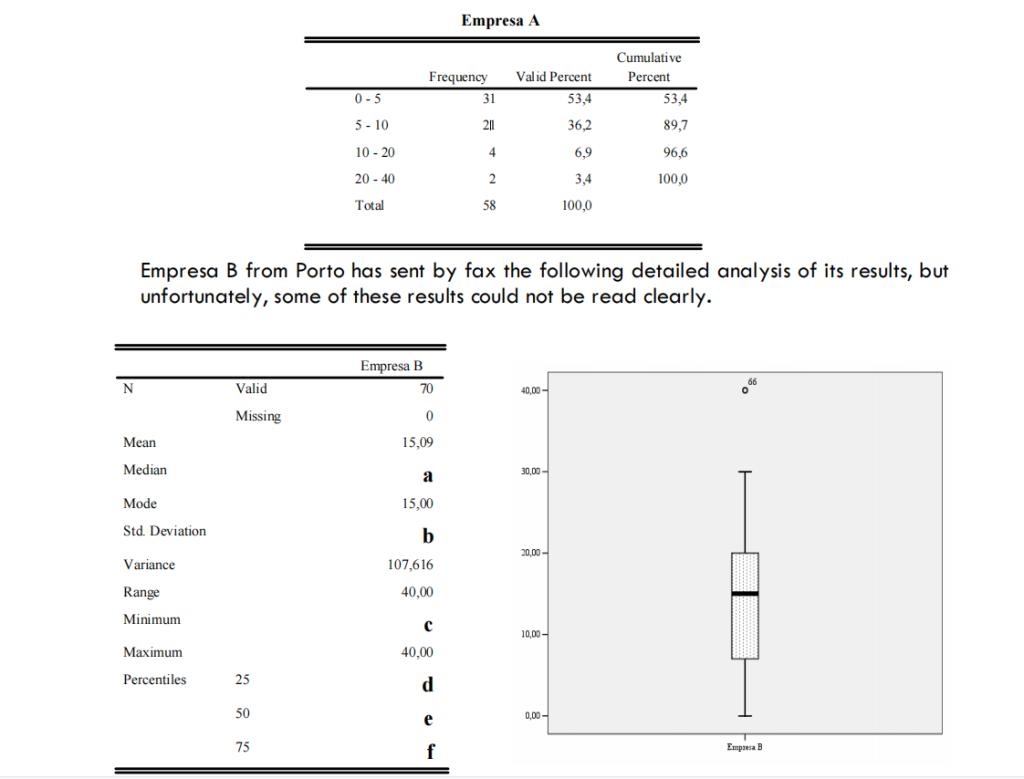
a) Calculate the values which are missing from the table of Empresa B and interpret the results presented in the table and in the graph.
b) Comment the accuracy of the following statements, justifying your comments.
b1) In Empresa A, the most frequent delay is 12 minutes.
b2) The mean delay is higher in Empresa A than in Empresa B.
b3) The distribution of delays presents a higher dispersion in Empresa A than in Empresa B.
(4,0) Since 2002 a survey has been conducted on a sample of Portuguese households about the use of new technologies. Some of the data from this study was used to study the adherence to e-commerce. The following annual values were obtained for the percentage of households linked to internet and also for an indicator of e-commerce
(Table 1). After adjusting this data with a simple linear regression model, results of Table 2 were obtained.
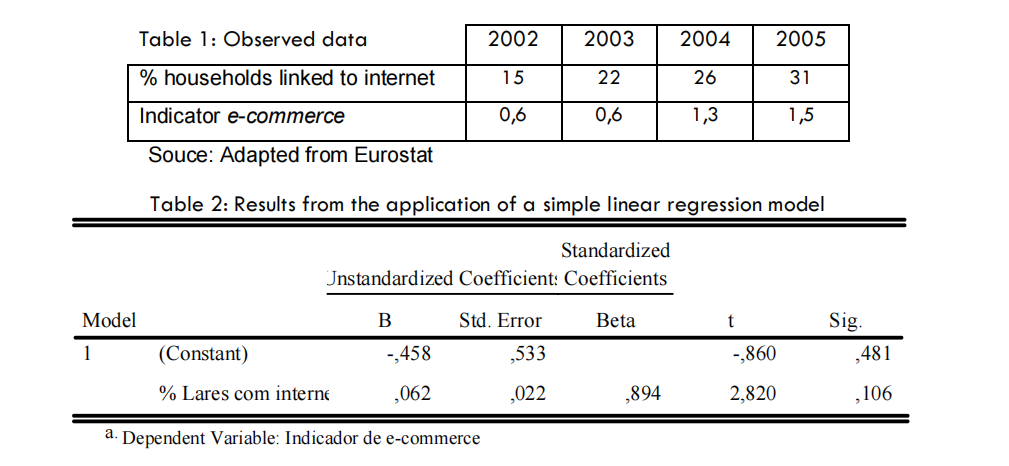
a) Calculate the correlation between the two variables.
b) Draw a scatterplot with the observed data and the adjusted line found with the ordinary least squares method. Comment the quality of this adjustment.
(3,0) Consider the following events A and B independent with probabilities 0,5 e 0,2, respectively.
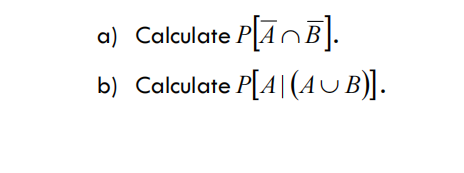
(8,0) A shirt producing company classifies the shirts they produce into three categories according to their finishing quality: “Good”, “Sufficient” and “Not sufficient”. Each shirt has a production cost of 2.50 euros. Shirts classified in the “Not sufficient” category correspond to 20% of the total production and are offered to beneficence institutions. 60% of the total production is sold with profit; this happens with 66% of the shirts with “Sufficient” quality and with 90% of the “Good” quality shirts.
a) Calculate the probability that a random chosen shirt has “Good” finishing quality.
b) Calculate the proportion of “Good” quality shirts within those that are sold with profit.
c) Assume now that the selling price of “Sufficient” quality shirts is 7.50 euros and that each shirt with category “Good” is sold by 10 euros. Consider the random variable “profit per shirt”.
c1) Define the probability function for this random variable.
c2) Define its distribution function. Using this function, calculate the probability of the profit per shirt being higher than 5 euros.
Note: If you didn’t solve a) assume that 40% of the shirts produced by this company have “Good” finishing quality.

更多代写:C/C++ 编程辅导 pte代考被抓 英国金融学网课作业代写 加拿大essay代写范文 加拿大paper写作 综述性论文代写
W6: Weekly quiz 统计quiz代考 Quiz Instructions This quiz will cover the asynchronous content from the Week 6 module. It is due BEFORE our synchronous class. Quiz Instructions This quiz ...
View detailsAMS 553.414/614: Applied Statistics and Data Analysis Practice questions for final exam 代考应用统计和数据分析 1. The data for this practice question is based on the cars dataset which is a...
View detailsST302 Stochastic Processes 随机过程考试代考 Each question has several subquestions, whose marks are shown in square brackets. Your answers should be justified by showing your work Suitable...
View detailsStatistics I Exam – 2nd sitting 统计exam代写 Please be reminded to define all the relevant random variables and quantities and justify your answers carefully. Please be reminded to defi...
View details